- info@venusautomations.com.au
INTERESTED IN A PRODUCT OR SERVICE?
Contact Now - We Respond Fast
- Monday – Friday: 8:30am to 5pm
Understanding Communication Protocols in PLCs
Introduction to PLC Communication Protocols
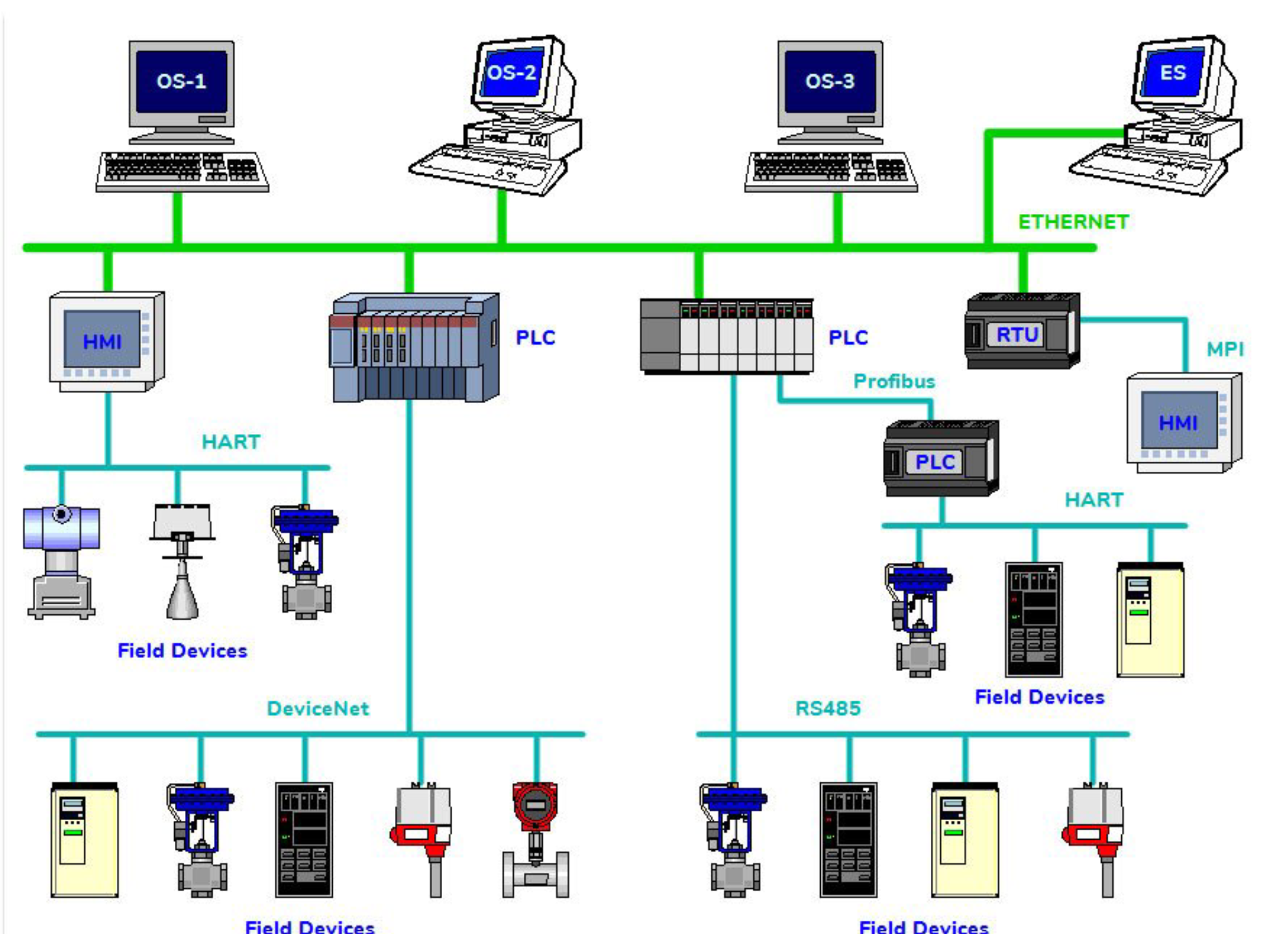
Programmable Logic Controllers (PLCs) constitute the backbone of industrial safety & automation, and it is through them that the integration of machines, sensors, and systems becomes seamless. For the operation of PLCs, however, they rely on communication protocols that facilitate data exchange among devices. Such protocols govern the structure, transmission, and reception of information as well as how they promote interoperability within complex industrial environments.
PLC communication protocols vary according to industry applications, the speed at which they must communicate, and hardware and software compatibility. These protocols are implemented on a massive scale, some of which are Modbus, PROFINET, EtherNet/IP, and CANopen. Modbus, a long-standing industrial protocol, is still used today because it is easy and reliable in exchanging data between PLCs and HMIs. Nevertheless, EtherNet/IP provides rapid data transfer over regular Ethernet networks, which makes it perfect for real-time industrial processes.
The selection of an appropriate PLC communication protocol is a function of the network topology, volume of data, and requirement for real-time processing. Industries such as manufacturing, automotive, and process control rely on them to achieve maximum efficiency, less downtime, and productivity. As industrial automation is still in its process of development, modern PLC communication protocols are including advanced networking features such as IIoT (Industrial Internet of Things) compatibility, accommodating more intelligent and interconnected industrial systems.
Importance of Communication Protocols in Automation
In modern industrial automation communication protocols are needed to deliver seamless interaction among machines, sensors, controllers, and enterprise systems. With standard communication lacking, automated systems would be beset with inefficiencies, errors, and operational bottlenecks, leading to increased downtime and lower productivity.
Communication protocols define how data is structured, transmitted, and processed across an industrial network. In multilevel plants, for example, programmable logic controllers (PLCs) must exchange real-time data continuously with human-machine interfaces (HMIs), robotic arms, and supervisory control and data acquisition (SCADA) systems. Protocols like PROFINET and EtherNet/IP support high-rate data transfer to guarantee that the machines operate efficiently and in harmony.
Reliability and security are also essential aspects of automation protocols. In the pharmaceutical and food processing sectors, strict compliance regulations require real-time monitoring and traceability of production data. Protocols like Modbus TCP/IP and OPC UA provide secure and efficient communication, allowing operators to monitor temperature, pressure, and quality metrics with minimal chance of data loss or corruption.
With continuous industrial automation, Industrial Internet of Things (IIoT) technologies integration is driving the demand for even more communication frameworks. Cloud analytics, remote monitoring, and predictive maintenance are being facilitated by the most recent protocols, thus reducing the likelihood of unforeseen failures and maximizing overall efficiency. By establishing high-quality communication protocols, industries can offer improved system interoperability, scalability, and long-term reliability with an extremely networked manufacturing environment.
Key PLC Communication Protocols
PLC communication protocols are required to achieve efficient data exchange between industrial automation devices. Protocols define how controllers, sensors, and machines communicate to achieve harmonious operation, real-time control, and system interoperability. Various protocols serve various industries based on speed, security, and compatibility with installed infrastructure. Mitsubushi also offers their internally-developed CC-Link system, with modules available for integration with PLC systems.
Ethernet/IP
Ethernet/IP (Industrial Protocol) is a widely used PLC communication protocol based on standard Ethernet technology. It offers real-time control and high-speed data transfer in industrial automation, which makes it ideal for applications such as robotics, motion control, and process automation. With support for TCP/IP and UDP/IP, Ethernet/IP allows easy integration into modern industrial networks.
The Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs all support Ethernet/IP, ensuring compatibility with industrial networks that require high-speed and reliable safety control communication. This allows seamless integration into environments using Rockwell Automation systems and other Ethernet-based controllers.
Modbus
Modbus is one of the oldest and most widely used PLC communication protocols. Originally developed for serial communication (Modbus RTU), it has evolved to support Ethernet-based communication (Modbus TCP/IP). It is commonly used for connecting PLCs, HMIs, and SCADA systems in industries such as manufacturing, energy, and building automation.
Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs support Modbus TCP, allowing them to communicate efficiently with SCADA systems, HMIs, and other industrial controllers over Ethernet. This enhances flexibility in multi-vendor automation environments.
Profibus
Profibus (Process Field Bus) is a fieldbus automation system protocol for communication between controllers and field devices such as sensors and actuators in a high-speed and reliable way. Profibus DP (Decentralized Peripherals) is utilized in factory automation, while Profibus PA (Process Automation) is utilized in process industries such as chemical and pharmaceutical processing.
Reer Mosaic safety PLCs support Profibus, enabling them to communicate with distributed automation devices in both process and factory automation applications. This allows for greater interoperability within legacy automation systems.
DeviceNet
DeviceNet is a robust industrial protocol used primarily in factory automation to connect PLCs with sensors, actuators, and other field devices. It was developed by Rockwell Automation and is based on CAN (Controller Area Network) technology, providing reliable, real-time communication with minimized wiring and network configuration.
While DeviceNet is widely used in industrial automation, the Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs primarily focus on Ethernet-based communication and do not natively support DeviceNet. However, gateways are available for integration if needed.
EtherCAT
EtherCAT (Ethernet for Control Automation Technology) is a highly rapid industrial Ethernet protocol that is optimized for high-performance automation control systems. It provides low-latency communications that are appropriate for applications that include high-precision synchronization, such as CNC machines, robotics, and motion control systems.
At present, the Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs do not natively support EtherCAT, as their primary focus is on standard Ethernet-based communication protocols such as PROFINET and Ethernet/IP. However, EtherCAT gateways can be used to enable integration in systems requiring high-speed motion control.
PROFINET
PROFINET is a robust industrial Ethernet standard designed for real-time automation. It offers Siemens high-speed data exchange, low latency, and high redundancy in the network. PROFINET is applied in high-reliability and deterministic communications sectors such as automobile manufacturing and big-scale process automation.
The Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs all support PROFINET, making them highly compatible with Siemens-based automation networks. This ensures fast and reliable communication for safety applications in complex manufacturing environments.
CANopen
CANopen is a communication protocol based on CAN (Controller Area Network) technology. It is commonly used in embedded automation applications, including automotive, medical devices, and industrial machinery. CANopen provides reliable data exchange with a well-defined application layer for standardized device communication.
Wieland samos® PRO, Reer Mosaic, and Pizzato Gemnis safety PLCs support CANopen, making them well-suited for applications requiring reliable distributed safety communication. This is particularly beneficial in industries such as automotive and specialized machinery, where robust, low-latency networking is essential.
Check Our Collections
SAMOS® PRO Compact Safety Controller
Discover the advanced SAMOS® PRO Compact Safety Controller, designed for reliable and efficient industrial safety automation.
Wieland samos SP-COP2-ENI-P-A
Wieland samos SP-COP2-ENI-A
Wieland samos SP-COP2-EN-P-A
Wieland samos SP-COP2-EN-IO-A
Pizzato GEMNIS Series
Explore the innovative Pizzato GEMNIS Series Safety Controllers, ensuring advanced safety and flexibility in industrial automation
Pizzato CS MP201M0 Safety Module
Pizzato CS MF201M0-P1 Safety Module
Pizzato CS MF202M0-P2 Safety Module
Pizzato CS MF202M0-P3 Safety Module
Pizzato CS MF202M0-P7 Safety Module
ReeR MOSAIC Series
“Discover the ReeR MOSAIC Safety PLC Series — a modular, high-performance platform ideal for managing complex safety systems with flexibility and precision.
MA4 Analog Input Unit – 1100025
MA4C Analog Input Unit – 1100125
MI12T8 Expansion Unit – 1100022
MI16 Expansion Unit – 1100021
MI8 Expansion Unit – 1100020
Factors Influencing Protocol Choice
Choosing the right PLC communication protocol is critical for building a robust and scalable industrial automation system. Multiple factors come into play, ranging from technical parameters to the physical environment and future scalability needs. These considerations directly affect system responsiveness, data integrity, and integration ease across machines, sensors, and controllers. Understanding these influences can help engineers and integrators select protocols—such as Modbus, PROFINET, or EtherCAT—that are not only compatible but optimized for the application’s demands.
Baud Rate Considerations
Baud rate, or communication speed, is one of the primary factors to consider when selecting a protocol. It determines how quickly data is transmitted between PLCs and connected devices. High-speed operations, like motion control or real-time monitoring, benefit from protocols that support higher baud rates such as EtherNet/IP or PROFINET. On the other hand, simpler systems that prioritize stability over speed, like Modbus RTU, may operate at lower baud rates but with reliable performance.
For instance, CANopen typically supports baud rates up to 1 Mbps, making it suitable for medium-speed, multi-node networks. Matching the baud rate with the capabilities of all devices in the network ensures smooth communication and minimizes data loss or collisions.